If you're still interested in sharing the RockChipBatchToolv1.3.zip file, then use any of the following sharing options to share it with anyone: Sharing Links. Unpacking is extracting update.img from releaseupdate.img, and then unpacking all the image files inside. While repacking, it is the inverse process. It synthesizes the image files described by the package-file, into update.img, which will be further packed together with the bootloader to create the final releaseupdate.img. Jun 27, 2018 Inside the zip file, you will find the SDFirmwareTool.exe and a Word Document with detailed instructions on how to use the Rockchip SD Firmware Tool correctly. Attention: Using the Rockchip SD Firmware Tool can also damage your device if not used correctly. This is a common guide for reflashing RockChip based devices. All RK SoC (RK3066, RK3188, RK3288, RK3229, RK3328, RK3399 and so on) supports the same applications and drivers for Host system, if 3rd party producers do not add any other limitations or special options. Previously I wrote an article entitled “How to Flash Rockchip RK3066 / RK3188 Firmware in Linux” explaining how to use a graphical tool called RkFlashKit to upgrade firmware on Rockchip devices using a Linux computer. This tool had some limitations, and it would just have a subset of features of RkAndroidTool (Windows), and it was not.
Rockchip Firmware Format¶
The rockchip firmware release_update.img, contains the boot loader loader.img and the real firmware data update.img:
release_update.img
update.img is packed with multiple image files, described by a control file named package-file. A typical package-file is:
package-file: packing description ofupdate.img, which is also included byupdate.img.Image/MiniLoaderAll.bin: The first bootloader loaded by cpu rom code.Image/parameter.txt: Parameter file where you can set the kernel boot parameters and partition layout.Image/trust.img: The Arm Trusted Image.Image/misc.img: misc partition image, used to control boot mode of Android.Image/kernel.img: Android kernel image.Image/resource.img: Resource image with boot logo and kernel device tree blob.Image/boot.img: Android initramfs, a root filesystem loaded in normal boot, contains important initialization and services description.Image/recovery.img: Recovery mode image.Image/system.img: Android system partition image.
Unpacking is extracting update.img from release_update.img, and then unpacking all the image files inside.
While repacking, it is the inverse process. It synthesizes the image files described by the package-file, into update.img, which will be further packed together with the bootloader to create the final release_update.img.
Installation of Tools¶
Unpacking Rockchip Firmware¶
Unpacking
release_update.img:Unpacking
update.img:Check the file tree in the update directory:
Packing Rockchip Firmware¶
First of all, make sure system partition in parameter.txt file is larger enough to hold system.img. You can reference Parameter file format to understand the partition layout.
For example, in the line prefixed with “CMDLINE” in parameter.txt, you will find the description of system partition similiar to the following content:
The heximal string before the “@” is the partiton size in sectors (1 sector = 512 bytes here), therefore the size of the system partition is:
To create release_update_new.img:
Customization¶
Customizing system.img¶
system.img is an ext4 file system format image file which can be mounted directly to the system for modification:
Note that the free space of system.img is almost 0. If you need to expand the image file, do adjust the partition layout in parameter.txt accordingly.
The following is an example of how to increase the size of the image file by 128MB.
Before expanding, make sure system.img is not mounted by running:
Resize the image file:
Boot Mode¶
eMMC flash is commonly soldered directly to the board. Some eMMC flash are pluggable, but it is hard to find a reader to use on PC. Therefore, eMMC is generally flashed onboard, that is, running to tiny system on the obard, which reads firmware data from PC and flashes to eMMC.
Depending on the existing data on the eMMC flash, there are two special boot modes: Rockusb Mode and Maskrom Mode.
You usually just need to enter Rockusb Mode for upgrading an existing Android OS or Firefly Ubuntu OS, which is packed with RK Firmware format.
Maskrom Mode is the last resort when Rockusb Mode is not available due to bootloader damage, or you need to flash Raw Firmware to eMMC.
Rockusb Mode¶
If the board powers on and finds a valid IDB (IDentity Block) in the eMMC, it will continue to load the bootloader from the eMMC and pass execution control to it. If the bootloader checks that the Recovery button is pressed and USB connection is made, then it enters the so-called Rockusb Mode, waiting for further instructions from the host.
Requirement:
5V2A power adapter.
Micro USB cable to connect power adapter and board.
Male to male USB cable to connect host PC and board.
eMMC.
Steps:
Pull all the USB cables (including micro USB cable and male to male USB cable) out of the board, to keep the board powering off.
Install the eMMC and pull out the SD card.
Use the male to male USB cable to connect the host PC with the USB 2.0 OTG port (the lower one in the double-decker ports) of the board.
Keep the RECOVERY button on the board pressed.
Plug in the micro USB cable to the board to power up.
Wait about 3 seconds before releasing the RECOVERY button.
Maskrom Mode¶
If anyone of the following conditions is met when the board powers on:
eMMC is empty.
The bootloader on eMMC is damaged.
eMMC read data failed by connecting eMMC data/clock pin to ground.
then no valid IDB (IDentity Block) will be found in the eMMC. The CPU will execute a small ROM code, waiting for the host to upload via USB a small DDR blob to initialize the DDR memory, and later a full bootloader to handle further firmware upgrading. This mode is called Maskrom Mode.
It involves hardware operation to force into MaskRom Mode, which has certain risk and should be carried out VERY CAREFULLY.
Requirement:
5V2A power adapter.
Micro USB cable to connect power adapter and board.
Male to male USB cable to connect host PC and board.
Metal tweezers to connect eMMC clock pin to ground.
eMMC.
Steps:
Pull all the USB cables (including micro USB cable and male to male USB cable) out of the board, to keep the board power off.
Install the eMMC and pull out the SD card.
Use a male to male USB cable to connect your host PC and USB OTG port of the board:
Find the reserved eMMC CLK and GND pads on the board, as shown below:
Connect the eMMC CLK and GND pads with metal tweezers and keep holding steadily.
Plug in the micro USB cable to the board to power on.
Wait about 1 seconds before releasing the metal tweezers.
Download Firmware¶
Firmware description: the firmware is classified into Raw Firmware and RK Firmware, which are placed into different folders. The latest firmware is the one with the latest date, which is often more stable. Please choose the correct tool to flash according to the type of firmware you need.
Linux (GPT) firmware: The Linux firmware files, including Ubuntu, Buildroot, Debian and other Linux systems, contain GPT in the filenames which means that they are using GPT partition scheme. They are referred to as Linux(GPT)firmware, which can be compiled in the Compile Linux firmware(GPT) chapter.
Flashing Instructions¶
The flashing tools and flashing methods used between different firmware are different. Please follow the table below to flash.
Flashing Tools¶
Please use the eMMC flashing tools according to your OS:
To flash to the eMMC:
GUI
AndroidTool (Windows)
CLI
upgrade_tool (Linux)
rkdeveloptool (Linux)
Tip:AndroidTool and upgrade_tool both support to flashing Raw Firmware and RK Firmware, But rkdeveloptool only support to flashing Raw Firmware.
AndroidTool¶
AndroidTool is used to flash Raw Firmware, RK Firmware and Partition Image to eMMC.
To use AndroidTool, you need to install Rockusb Driver first.
Installing Rockusb Driver¶
Download DriverAssistant, extract the archive and run DriverInstall.exe inside.
Click the “驱动安装” button to install the driver. If you want to uninstall the driver, click the “驱动卸载” button.
If your device is in Rockusb Mode or Maskrom Mode, you’ll find a RockusbDevice in the device manager:
Installing AndroidTool¶
Flashing tool selection and download:
Flashing Raw Firmware: AndroidTool_v2.39
Flashing RK Android7.1 Firmware: AndroidTool_v2.38
Flashing RK Android8.1 Firmware: AndroidTool_v2.58
Flashing RK Linux(GPT) Firmware: AndroidTool_v2.58
Download AndroidTool, extract it. Locate the file named config.ini, and edit it by changing the 4th line from Selected=1 to Selected=2, in order to select English as the default user interface language.
Launch AndroidTool.exe:
If your device is in Rockusb Mode, the status line will be “Found One LOADER Device”.
If your device is in Maskrom Mode, the status line will be “Found One MASKROM Device”.

Flashing Raw Firmware¶
Raw Firmware needs to be flashed to offset 0 of eMMC storage. However, in Rockusb Mode, all LBA writes are offset by 0x2000 sectors. Therefore, the device has to be forced into Maskrom Mode.
To flash Raw Firmware to the eMMC using AndroidTool, follow the steps below:
Force the device into Maskrom Mode.
Run AndroidTool.
Switch to the “Download Image” tab page.
Keep the first line of the table unchanged, using the default loader file.
Click the right blank cell on the second line, which will pop up a file dialog to open the Raw Firmware file.
Click the “Run” button to flash.
Flashing RK Firmware¶

To flash RK Firmware to the eMMC using AndroidTool, follow the steps below:
Force the device into Rockusb Mode or Maskrom Mode.
Run AndroidTool.
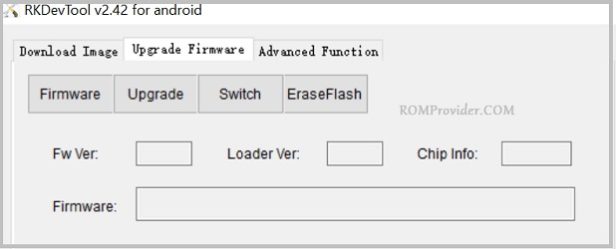
Switch to the “Upgrade Firmware” tab page.
Click the “Firmware” button, which will pop up a file dialog to open the RK Firmware file.
The firmware version, loader version and chip info will be read and displayed.
Click the “Upgrade” button to flash.
Tips:If you want to flash different system or fail to flash, please read Flashing Instructions carefully.
Flashing Partition Image¶
Depending on the original firmware of the development board, flashing the partition image to eMMC will be different.
To flash Partition Image to the eMMC using [AndroidTool_v2.39], follow the steps below:
Force the device into Rockusb Mode or Maskrom Mode.
Run AndroidTool.
Switch to the “Download Image” tab page.
Keep the first line of the table unchanged.
Delete all others unused rows by selecting “Delete Item” from the right-click popup menu.
Add partition image to flash by selection “Add Item” from the right-click popup menu.
Check on the checkbox on the first cell.
Fill in the address with the sector offset (plus
0x2000if in Maskrom Mode) of partition inparameter.txtfile.Click the right blank cell to browse to the Partition Image file.
Click the “Run” button to flash.
Note:
You can add multiple partitions to flash by repeating step 6.
You can skip the partition flashing by checking off the checkbox in front of the address cell.
In Maskrom Mode, you must add
0x2000to the sector offset of the partition inparameter.txt. See Partition Offset for more detail.
Use AndroidTool_v2.38 to flashing RKAndroid7.1 firmware partitions with default configuration.
Use AndroidTool_v2.58 to flashing RKAndroid8.1 firmware partitions with rk3328-Android81.cfg configuration, Right-click the blank section, click loadconfig, and select the corresponding configuration file.
Use AndroidTool_v2.58 to flashing RKLinux(GPT) firmware partitions with default configuration.
To flash Partition Image to the eMMC using AndroidTool, follow the steps below:
Force the device into Rockusb Mode.
Run AndroidTool.
Switch to the “Download Image” tab page.
Make sure the path to the image file is correct. If necessary, click the blank table cell to the right of the path to reselect it.
Click the “Run” button to start the upgrade. After the upgrade, the device will restart automatically.
upgrade_tool¶
upgrade_tool is a close-sourced command line tool provided by Rockchip, which supports flashing Raw Firmware, RK Firmware and Partition Image to the eMMC.
Installing upgrade_tool¶
Flashing tool selection and download:
Flashing Raw Firmware or
Android7.1: upgrade_tool_v1.24Flashing RK Firmware or
Android8.1: upgrade_tool_v1.34
Download upgrade_tool, and install it to your Linux host:
Then add udev rules by instructions here, in order to have permission for the normal user to flash Rockchip devices. If you skip this, you must prefix the following commands with sudo to have the right permission.
Flashing Raw Firmware¶
Raw Firmware needs to be flashed to offset 0 of eMMC storage. However, in Rockusb Mode, all LBA writes are offset by 0x2000 sectors. Therefore, the device has to be forced into Maskrom Mode.
To flash Raw Firmware to the eMMC using upgrade_tool, follow the steps below:
Force the device into Maskrom Mode.
Run:
Note:
rk3328_loader_ddr786_v1.06.243.binis the copied loader file after compilingU-Boot. It can also be downloaded from here (chooserk3328_loader_xxx.binfile).system.imgis Raw Firmware after packing, which can also be Raw Firmware downloaded from official site (decompress first).
Flashing RK Firmware¶
Rockchip Upgrade_tool
To flash RK Firmware to the eMMC using upgrade_tool, follow the steps below:
Force the device into Rockusb Mode or Maskrom Mode.
Run:
if the upgrade failed, please erase the eMMC:
Flashing Partition Image¶
You can write individual Partition Image to the eMMC. Depending on the original content of the eMMC, the instructions can be somewhat different.
Raw Firmware
If the original firmware format is raw, chances are that it is using the GPT partition scheme, and the predefined offset and size of each partition can be found in build/partitions.sh in the SDK. See Partition Offset for more detail.
To flash Partition Image to the eMMC using upgrade_tool, follow the steps below:
Force the device into Maskrom Mode.
Use upgrade_tool to flash the Partition Image:
RK Firmware
If the original firmware format is Rockchip, it is using the parameter file for partition scheme, and you can use the partition name to flash Partition Image directly.
To flash the Partition Image to the eMMC using upgrade_tool, follow the steps below:
Force the device into Rockusb Mode.
Use upgrade_tool to flash the Partition Image:
Android7.1
Android8.1
Linux(GPT)
Note:
-bis a predefined shortcut forbootpartition. If no shortcuts are available, use partition name instead (resourcein above example).You can customize kernel parameters and partition layout according to Parameter file format. Once the partition layout is changed, you must flash the
parameterfile first, before reflashing other changed partitions.
FAQ¶
If errors occur due to flash storage problem, you can try to low format or erase the flash by:
Rockchip Create Upgrade Disk Tool V1.53
rkdeveloptool¶
rkdeveloptool is an open-source command line flashing tool developed by Rockchip, which is an alternative to the close-source upgrade_tool.
rkdeveloptoolDOES NOT support proprietary RK Firmware.
Installing rkdeveloptool¶
First, download, compile and install rkdeveloptool:
Then add udev rules by instructions here, in order to have permission for the normal user to flash Rockchip devices. If you skip this, you must prefix the following commands with sudo to have the right permission.
Flashing Raw Firmware¶
Raw Firmware needs to be flashed to offset 0 of eMMC storage. However, in Rockusb Mode, all LBA writes are offset by 0x2000 sectors. Therefore, the device has to be forced into Maskrom Mode.
To flash Raw Firmware to the eMMC using rkdeveloptool, follow the steps below:
Rockchip Upgrade_tool Tablet
Force the device into Maskrom Mode.
Run:
Note:
rk3328_loader_ddr786_v1.06.243.binis the copied loader file after compilingU-Boot. It can also be downloaded from here (chooserk3328_loader_xxx.binfile).system.imgis Raw Firmware after packing, which can also be the Raw Firmware downloaded from official site (decompress it first).
Flashing Partition Image¶
The following instructions ONLY APPLIY to boards which are flashed with Raw Firmware and use GPT partition scheme. The predefined offset and size of each partition can be found in build/partitions.sh in the SDK. See Partition Offset for more detail.
To flash Partition Image to the eMMC using rkdeveloptool, follow the steps below:
Force the device into Maskrom Mode.
Run:

udev¶
Create /etc/udev/rules.d/99-rk-rockusb.rules with following content1. Replace the group users with your actual Linux group if neccessary:
Reload the udev rules to take effect without reboot:
Partition Offset¶
GPT Partition¶
The offset of partition image can be obained by following command(assuming you are in the directory of Firefly Linux SDK):
which gives result of:
parameter¶
If RK Firmware is used, parameter.txt is used to define partition layout.
Here’s a handy script to list the partition offsets in parameter.txt:
Save it as a script in /usr/local/bin/show_rk_parameter.sh and give the script executing permission.
Here’s an example of showing partition offsets defined in RK3328AndroidSDK: